Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental health disorder that affects between 1.6% and 2.5% of the population, according to the Yale School of Medicine. People with the disorder experience obsessive and intrusive thoughts that often trigger anxiety and distress. They may then engage in compulsive behaviors to manage discomfort until the obsessive thoughts return, continuing the cycle.
Even though compulsions provide temporary relief, they can be detrimental, often taking up so much time that it’s difficult for people with OCD to function in daily life (per Healthline). For some who have struggled with acne and other skin conditions, this pattern may sound familiar. Many people find it difficult to refrain from popping and picking at blemishes, dry skin, and other marks on the body. One 2024 survey by OnePoll and the beauty brand Truly Beauty even found that over 80% of American women admit to popping their pimples — despite the fact that most dermatologists urge against it (per Medical News Today).
Here’s the connection between skin picking and OCD and how to tell the difference between the two.
The link between skin picking and OCD
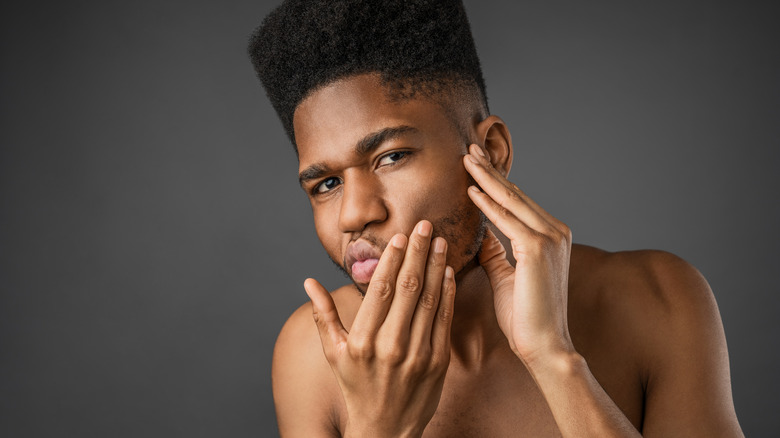

According to the International OCD Foundation, picking at scabs, dry spots, and zits doesn’t always signal OCD. Most people occasionally pick or scratch at spots on their skin. However, skin picking may be considered a disorder if it’s highly repetitive, causes tissue damage, or interferes with overall well-being.
A skin picking disorder may be classified as an impulse control disorder. However, the 5th edition of the “Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders,” which sets the benchmark for diagnosing and recognizing mental conditions, also defines it as a type of OCD (per Healthline). Even when diagnosed separately from OCD, the two often coincide. Cleveland Clinic explains that people who compulsively pick at their skin are likely to have other mental health conditions, too, including OCD and anxiety.
There are some differences between a skin picking disorder and general OCD, however. While OCD focuses heavily on obsessions, a skin picking disorder doesn’t. Compulsive skin picking can also result in damage to the skin and body, which isn’t typical in most other types of OCD.
How to treat a skin picking disorder
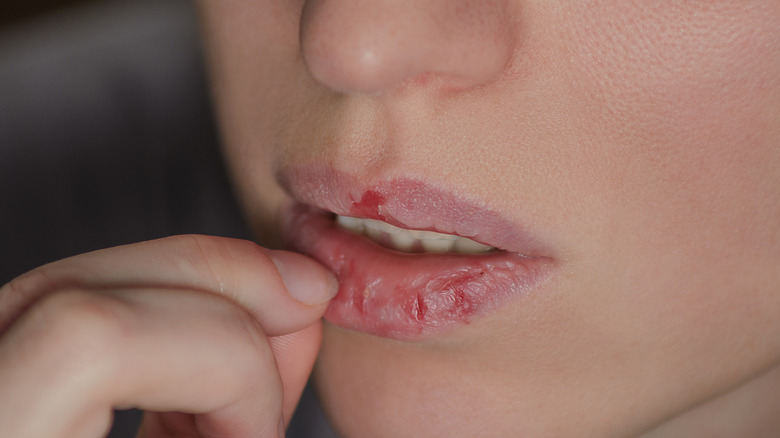
While a skin picking disorder may be related to OCD, it can require different treatments. One 2024 study published in Focus suggested that behavioral therapies are the most effective treatment for skin picking, as well as compulsive hair pulling. This is similar to cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and other psychotherapy treatments offered to people with OCD (per Mayo Clinic). However, Cleveland Clinic explains that a skin-picking disorder is often triggered by a separate condition — such as a bothersome skin condition — while Healthline notes the possible connection between autoimmune diseases and skin picking. Some people may also pick at imperfections on their skin as part of body dysmorphic disorder (per NOCD).
Identifying and managing comorbid physical and mental health conditions is a crucial part of treating compulsive skin picking. People with the disorder can also self-manage symptoms by identifying and avoiding triggers, keeping their hands occupied with an object or activity, and maintaining clean skin to discourage picking and prevent infection (per NHS).



